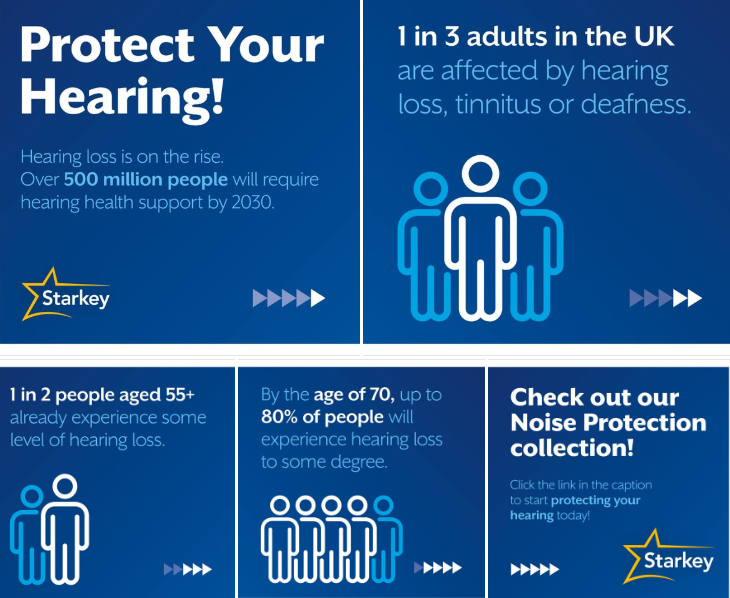
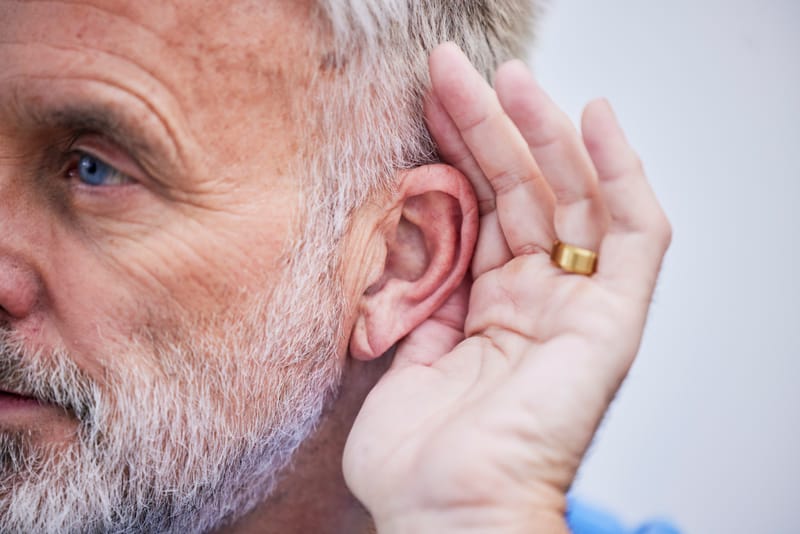
Hear the World Clearly,
Empowering Lives Through Better Hearing.
At Hylands Hearing my mission is to enhance the quality of life for individuals through improved hearing. I am dedicated to providing comprehensive hearing care services, including professional ear wax removal, hearing assessments, and advanced hearing aid solutions. I strive to make these essential services accessible and affordable for everyone, ensuring that cost is never a barrier to better hearing. By prioritizing compassionate care and innovative hearing solutions, empowering my clients to enjoy the full spectrum of sounds and experiences that life has to offer.
Sarah Hylands-Thorpe
Hearing Aid Audiologist; HCPC Reg No: HAD03165.

10% off all level 24 mobels
Omega AI 24 RIC R £450 off
plus a free Remote Control worth £99.00
Edge AI 24 RIC R £400 off
plus a free Remote Control worth £99.00
Genesis AI 24 RIC R £350 off
plus a free Remote Control worth £99.00
Evolv AI 24 RIC R £300 off
plus a free Remote Control worth £88.00
Services
We strive to make hearing aids affordable for everyone, ensuring that cost is never a barrier to better hearing.
Hearing Health Check
A hearing health check is a comprehensive evaluation of an individual's hearing function and ear health, it identify and diagnose hearing issues: 1. Otoscopy is a visual examination of the outer ear canal and eardrum. An otoscope (a device with a light and magnifying lens) is used to look inside the ear. It can identifies earwax buildup, infections, eardrum perforations, or other abnormalities in the ear canal and eardrum. 2. Weber and Rinne Tuning Fork Tests These tests can differentiate between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. Weber Test: A vibrating tuning fork is placed on the center of the forehead. The patient indicates where they hear the sound best (in the middle, left, or right ear). Rinne Test: A vibrating tuning fork is placed on the mastoid bone (bone conduction) and then near the ear canal (air conduction). Normally, air conduction is better than bone conduction (positive Rinne). A negative Rinne (bone conduction better than air) indicates conductive hearing loss. 3. Tympanometry assess the function of the middle ear. A probe is placed in the ear canal, varying air pressure to move the eardrum. What It Measures: Eardrum movement (compliance), ear canal volume, and middle ear pressure. This identifies fluid in the middle ear, eardrum perforations, eustachian tube dysfunction, or ossicular chain problems. 4. Warble Box Free Field Hearing Test Evaluate hearing ability without the use of a full audiometric hearing test . Warble tones (frequency-modulated sounds) are presented through speakers. Sounds at different volumes and frequencies are presented to the client and the clients responses are recorded. The results estimate hearing thresholds and checks the functional hearing ability in a natural listening environment. Together, these tests provide a detailed understanding of an individual's hearing health, ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning. Cost £30.00.
Full Audiometric Hearing Assessment
A telephone consultation is completed prior to all Hearing Assessments. A Hearing Assessment includes a Hearing Hearth Check. Pure tone audiometry is a standard hearing test used to measure an individual's hearing sensitivity across various frequencies. Here’s a brief summary of the process and its significance: Purpose Assess Hearing Sensitivity: Determines the softest level of sound that a person can hear at different pitches (frequencies). Diagnose Hearing Loss: Helps identify the degree, type, and configuration of hearing loss. Procedure: Testing Air Conduction: Presentation of Tones are presented to the individual through headphones: Pure tones of varying frequencies (typically 250 Hz to 8000 Hz) are presented one ear at a time. Response: The individual signals (e.g., pressing a button) when they hear a tone. Threshold Determination: The lowest intensity level (measured in decibels, dB) at which the tone is heard 50% of the time is recorded as the hearing threshold for that frequency. Testing Bone Conduction: A bone vibrator is placed on the mastoid bone behind the ear to bypass the outer and middle ear, directly stimulating the inner ear. This helps distinguish between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. Results Audiogram: The results are plotted on an audiogram, a graph that shows hearing thresholds across frequencies for both air and bone conduction. Hearing Loss Classification: Normal Hearing: 0-25 dB Mild Hearing Loss: 26-40 dB Moderate Hearing Loss: 41-55 dB Moderately Severe Hearing Loss: 56-70 dB Severe Hearing Loss: 71-90 dB Profound Hearing Loss: 91+ dB Importance Early Detection: Identifies hearing issues early, enabling timely intervention. Monitoring: Tracks changes in hearing over time, particularly in individuals exposed to noise or those with progressive hearing loss conditions. Pure tone audiometry is a critical tool in audiology, providing detailed insights into an individual's hearing health and guiding effective management strategies. Cost £80.00. Or £50.00 if you have already completed a Hearing Health Check.
Hearing Solution
An appropriate hearing aid solution is crucial for several reasons: 1. Improved Communication Enhanced Understanding: Helps individuals hear and understand speech better, especially in challenging environments. Social Interaction: Facilitates more effective communication, reducing social isolation and improving relationships. 2. Quality of Life Increased Independence: Enables individuals to perform daily activities more effectively, fostering greater independence. Mental Health: Reduces feelings of frustration, embarrassment, and depression associated with hearing loss. 3. Cognitive Health Cognitive Function: Aids in maintaining cognitive functions by keeping the brain engaged through auditory stimulation. Delay Cognitive Decline: Prevents accelerated cognitive decline and dementia linked to untreated hearing loss. 4. Safety Environmental Awareness: Improves awareness of surroundings, which is vital for personal safety (e.g., hearing alarms, traffic sounds). 5. Customized Fit and Comfort Tailored Solutions: Ensures that the hearing aid fits well and is comfortable, leading to consistent use. Specific Needs: Addresses the specific type and degree of hearing loss, providing the most effective amplification and clarity. 6. Technological Benefits Advanced Features: Modern hearing aids offer features like noise reduction, Bluetooth connectivity, and directional microphones, enhancing overall listening experiences. Adaptability: Can be adjusted and fine-tuned to adapt to various listening environments and individual preferences. 7. Long-Term Hearing Health Ongoing Management: Properly fitted and regularly maintained hearing aids can help manage and potentially slow the progression of hearing loss. In summary, an appropriate hearing aid solution is vital for improving communication, quality of life, cognitive health, safety, and overall well-being, ensuring that individuals with hearing loss can lead fuller, more engaged lives. Hearing Aids Starting price £380.00.
Fitting
A Hearing Aid Fitting appointment is a crucial step in the process of addressing hearing loss. The main purposes of this appointment are: 1. Customization Personalized Adjustment: Tailors the hearing aid settings to the individual's specific hearing loss profile, ensuring optimal performance. Comfort Fit: Ensures that the hearing aid fits comfortably in or on the ear, preventing discomfort and ensuring consistent use. 2. Instruction and Training Device Operation: Educates the user on how to operate the hearing aid, including turning it on and off, changing batteries, and using special features. Maintenance: Provides guidance on cleaning, maintaining, and troubleshooting the device to ensure its longevity and reliability. 3. Programming and Fine-Tuning Sound Quality: Adjusts the sound quality and volume levels to meet the user's preferences and needs in various environments. Feedback Reduction: Addresses any issues with feedback or other sound distortions to improve overall listening experience. 4. Verification and Validation Real-Ear Measurements: Conducts real-ear measurements to verify that the hearing aid delivers the correct amount of amplification. Performance Check: Ensures that the hearing aid meets the prescribed targets and provides effective hearing improvement. 5. Counseling and Support Expectation Management: Discusses realistic expectations regarding the hearing aid's performance and the adaptation process. Support Resources: Provides information about support resources, follow-up appointments, and any available assistive listening devices. 6. User Comfort and Satisfaction Initial Comfort: Ensures that the user feels comfortable and confident with their new hearing aid. Address Concerns: Addresses any immediate concerns or questions the user may have about their new device. In summary, a Hearing Aid Fitting appointment is essential for customizing the device to the user's needs, providing necessary training and support, ensuring optimal device performance, and promoting user comfort and satisfaction. 60-Day Money Back Guarantee.
Follow-Up
Hearing aid follow-up appointments are essential for ensuring the long-term success and satisfaction of hearing aid users. The main purposes of these appointments are: 1. Fine-Tuning and Adjustment Performance Optimization: Adjust hearing aid settings to improve performance based on the user’s experiences in different listening environments. Addressing Issues: Resolve any problems the user may encounter, such as feedback, discomfort, or difficulty hearing specific sounds. 2. Monitoring and Evaluation Progress Assessment: Evaluate the user's progress with the hearing aids and ensure they are meeting the user's hearing needs and expectations. Hearing Check: Monitor any changes in hearing and adjust the hearing aid settings accordingly. 3. Maintenance and Care Device Check: Inspect the hearing aids for any signs of wear and tear, and perform necessary maintenance tasks like cleaning and replacing parts. User Guidance: Provide additional instruction on proper care and use of the hearing aids to extend their lifespan and effectiveness. 4. Support and Counseling Ongoing Support: Offer continued support and counseling to help the user adapt to and become comfortable with their hearing aids. Address Concerns: Discuss any new concerns or questions the user may have, providing reassurance and solutions as needed. 5. Technology Updates Software Updates: Update the hearing aid software to the latest version, ensuring optimal performance and access to new features. Feature Training: Educate the user on new features or functionalities that may have been added through updates. 6. Long-Term Satisfaction User Feedback: Gather feedback from the user to ensure they are satisfied with their hearing aids and to make any necessary adjustments. Lifestyle Changes: Adjust the hearing aids to accommodate any changes in the user’s lifestyle or hearing needs. In summary, hearing aid follow-up appointments are crucial for ensuring that the hearing aids continue to meet the user’s needs, providing ongoing support and maintenance, and optimizing the overall hearing experience. Free Follow Up appointments within the 60-Day Money Back Guarantee period.
Aftercare
Aftercare appointments for hearing aids are crucial for several key reasons: 1. Optimal Performance Fine-Tuning: Ensure the hearing aids are properly adjusted to the user's changing hearing needs and environments. Software Updates: Keep the devices updated with the latest software for improved functionality and performance. 2. Maintenance and Longevity Routine Checks: Identify and address any wear and tear or technical issues before they become significant problems. Cleaning and Repairs: Provide professional cleaning and minor repairs to keep the hearing aids in good working condition. 3. User Adaptation and Comfort Addressing Discomfort: Adjust fit and settings to resolve any issues causing discomfort or irritation. Enhancing Experience: Improve user experience based on feedback about sound quality and device performance. 4. Continuous Support and Education Ongoing Training: Offer guidance on the best practices for using, maintaining, and troubleshooting hearing aids. Counseling: Provide support for any psychological or emotional challenges related to hearing loss and hearing aid use. 5. Monitoring Hearing Health Hearing Assessments: Regularly check hearing levels to detect any changes and adjust hearing aid settings accordingly. Preventing Further Loss: Advise on protective measures to prevent further hearing deterioration. 6. Maximizing Benefit User Satisfaction: Ensure the user is getting the maximum benefit from their hearing aids, leading to higher satisfaction and consistent use. Quality of Life: Enhance overall quality of life by maintaining effective hearing aid performance, which supports better communication and social interaction. In summary, aftercare appointments are essential for maintaining the functionality, comfort, and effectiveness of hearing aids, ensuring that users receive ongoing support and optimal benefit from their devices. Cost dependant on chosen solution.
Hearing Aids & Accessories
We strive to make hearing aids affordable for everyone, ensuring that cost is never a barrier to better hearing.
Widex: Less is more with natural hearing.
Forget your hearing loss with natural sound for natural hearing.
Signia: Because hearing what matters has never been more important in today’s busy world, where a missed word can mean a missed opportunity.
Presbycusis (Age-Related Hearing Loss)
- Degeneration of Inner Ear Structures:
- Damage to hair cells in the cochlea, which play a key role in converting sound waves into electrical signals for the brain.
- Changes in the Auditory Nerve:
- Reduced ability of the auditory nerve to transmit signals effectively.
- Circulatory System Changes:
- Reduced blood flow to the inner ear, affecting its function.
- Environmental Factors:
- Long-term exposure to loud noises can accelerate hearing loss.
- Genetic Predisposition:
- Family history of hearing loss may increase risk.
- Difficulty hearing high-pitched sounds (e.g., birdsong or women's voices).
- Trouble understanding speech, especially in noisy environments.
- Perception that others are mumbling or speaking unclearly.
- Needing to increase the volume on televisions or radios.
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus) may also accompany presbycusis.
- Hearing Tests: Audiometry to assess the range and degree of hearing loss.
- Medical History and Examination: Identifying contributing factors like noise exposure or family history.

Private clinics often have significantly shorter waiting times for appointments, than the NHS.
Private hearing aids typically offer enhanced sound processing and noise reduction technologies, resulting in better sound quality. These devices can be tailored more precisely to an individual’s hearing loss and lifestyle.
Many private models come with Bluetooth, enabling seamless integration with smartphones, TVs, and other devices.
Private hearing aids often have more aesthetic options, including nearly invisible in-ear models.
Private audiologists usually provide more personalized and thorough care, including follow-ups and adjustments to ensure the hearing aids are optimally tuned.
Private providers offer a broader selection of hearing aid models, giving users more options to find the perfect fit.
Users can choose hearing aids based on their appearance as well as preferences, ensuring comfort and satisfaction.
Private providers often have quicker access to the latest advancements in technology, benefiting individuals from cutting-edge features. Many private providers offer trial periods or return policies, allowing users to test different models before making a final decision.
While NHS hearing aids provide essential and often free or low-cost services to many people, but they come with limitations.
Longer waiting times for appointments and follow-ups.
Generally the NHS provide basic models with essential features. They are effective for most hearing loss types but may lack advanced functionalities. Less advanced and customizable technology. With fewer models and brands to choose from.
Less frequent follow-ups and adjustments.
Summary
Opting for private hearing aids offers several advantages over NHS options, particularly in:
Technology: Access to advanced and customizable hearing aids.
Service: More personalized care and better customer support.
Convenience: Reduced waiting times and flexible scheduling.
These benefits can significantly enhance the overall user experience, making private hearing aids a worthwhile consideration for those seeking the best in hearing care.
At Hylands Hearing our starting price for Private Hearing aids is not as expensive as you think, £500.00.
For more information and to schedual an appointment vist:
https://www.earwaxremoval.me
Contact
We strive to make hearing aids affordable for everyone, ensuring that cost is never a barrier to better hearing.
- Clinic's in Callington, Launceston, Liskeard, Saltash.
- Home visits available for those unable to travel. For more information get in contact.
- +44-07494454613
- hylandsthorpe@yahoo.co.uk
- Mon-Fri - 09:00-17:00
By appointment only. Home visits are not available for ear wax removal treatments, please visit www.earwaxremoval.me
Blog
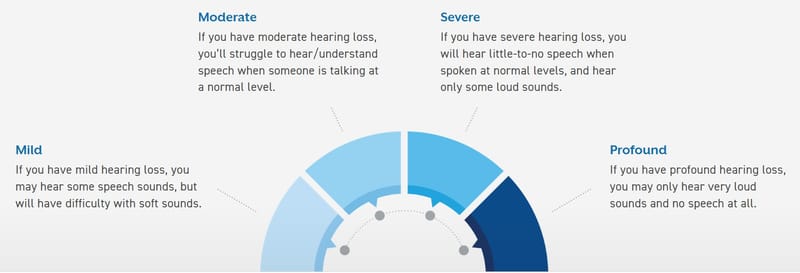
Degree of hearing loss.
Degrees of hearing loss. There are four clinically labeled degrees of hearing loss: Mild; Moderate; Server and Profound.
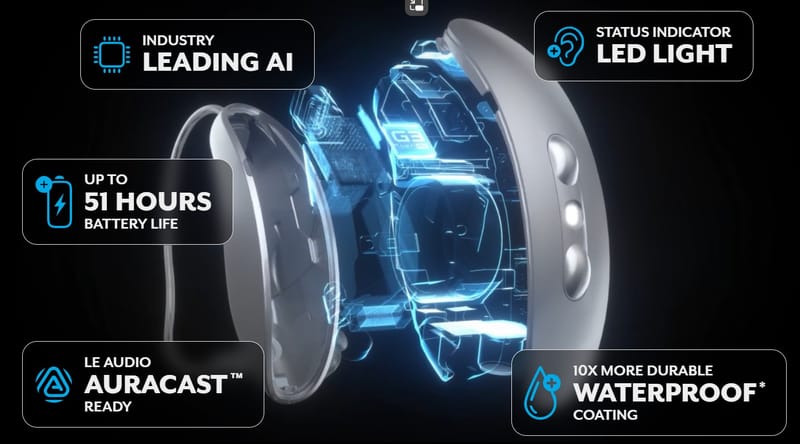
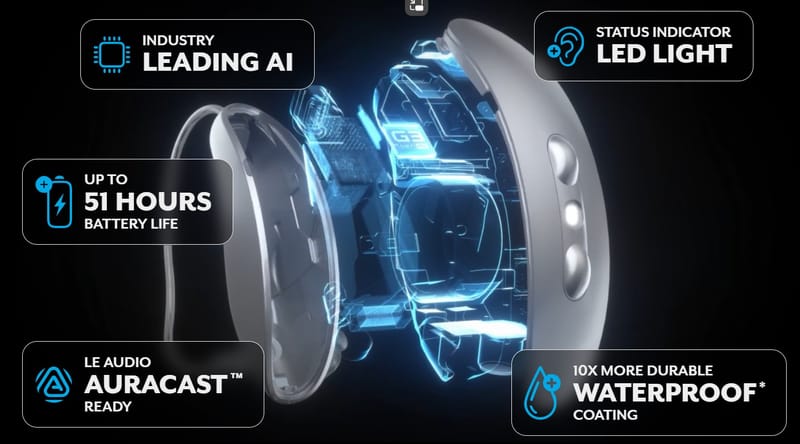
Starkey Omega AI: “Technology so intelligent, it’s superhuman”
Starkey Omega AI: “Technology so intelligent, it’s superhuman” Starkey has long been recognised as a pioneer in hearing aid technology, particularly in bringing artificial intelligence (AI) and sensor based “healthable” features into devices. With their latest flagship line Omega AI they’ve once again raised the bar. Launched in October 2025, Omega AI is described as what the company sees as a new gold standard in hearing aids: stronger sound clarity, better connectivity, enhanced durability, and wellness tools built in. In this blog post, we’ll explore:
Most causes of hearing loss are impossible to prevent. However, noise-induced hearing loss is not
Most causes of hearing loss are impossible to prevent. However, noise-induced hearing loss is not.
How your ear health affects your balance:
Hearing and balance are closely connected because they both rely on the inner ear specifically, the cochlea for hearing and the vestibular system for balance. When one part is affected, the other often is too. As we age, it's common for both hearing and vestibular function to decline, leading to an increased risk of dizziness, unsteadiness, and even falls. This is why many people with hearing loss also report balance issues. Understanding this connection is vital for effective diagnosis and treatment. Both hearing and balance, ensuring a holistic approach to your ear health. If you're experiencing hearing changes alongside dizziness or instability, it may be more than coincidence—and getting professional help could make all the difference.
✈️ Travelling with Hearing Loss: Tips for a Smooth Journey with Hearing Aids
🧳 Final Thoughts: Travel with Confidence With a bit of forward planning and care, hearing loss doesn’t have to get in the way of your adventures. Modern hearing aids offer amazing flexibility and control, and with the right support, you’ll be free to enjoy every moment — from boarding calls to beach conversations. If you have questions about ear health or hearing before your next trip, we’re here to help.
Why Choose an Independent Hearing Aid Audiologist Over High Street Chains?
If you’re considering hearing aids or seeking better hearing care, an independent audiologist is a fantastic choice. With personalized service, access to a broader range of hearing aids, superior aftercare, and genuine patient-focused care, independent audiologists offer a level of expertise and attention that high street chains simply cannot match. When it comes to your hearing, why settle for anything less than the best? Support your local independent audiologist and experience the difference today!
How Untreated Hearing Loss Affects Your Health and Quality of Life
How Untreated Hearing Loss Affects Your Health and Quality of Life
Signs You Might Have Hearing Loss – And What to Do About It
Signs You Might Have Hearing Loss – And What to Do About It
The Connection Between Hearing Loss and Dementia: Understanding the Link
The Connection Between Hearing Loss and Dementia: Understanding the Link